On 10 October Frontex released its FRAN (Frontex Risk Assessment Network) Quarterly Report for the Second Quarter of 2012 (April-June). As is always the case, the 70 page report contains a significant amount of information, graphs, and statistical tables regarding detections of illegal border crossings (land, air, and sea), irregular migration routes, detections of facilitators, detections of illegal stays, refusals of entry, asylum claims, returns, information regarding other illegal border activities, and more. Here are some highlights (focusing on the sea borders):
Malta- There was a significant increase in the number of Somalis reaching Malta. “Taking into account the professional planning of the trips, it is assumed that the modus operandi has changed and that Malta is now targeted on purpose, thereby replacing Italy as the preferred destination country for this nationality. The reason for this change has not yet been confirmed; however, in the past Malta resettled some Somali migrants in the United States and in some EU Member States, which might be acting as a pull factor.”
Spain- “In this region there was a new modus operandi involving facilitators dropping off migrants in the Chafarinas Islands, a Spanish archipelago 2 nautical miles away from the Moroccan coastline.”
“As reported in the previous FRAN Quarterly, in February 2012 Moroccan and Spanish Ministers of Interior signed a police agreement to create two joint police stations in the Spanish (Algeciras) and Moroccan (Tangiers) territories to cooperate by exchanging operational information and best practices between different police services.”
Italy- “Throughout the quarter, Italy and Tunisia cooperated efficiently to repatriate Tunisian nationals and so most migrants typically arrived undocumented to delay readmission.”
Central Mediterranean- “[D]etections in the Central Mediterranean showed a seasonal increase but were much reduced (-86%) compared with the dramatic peak during the same period in 2011. Indeed, in the second quarter of 2012 detections in this region resembled the pre-Arab Spring levels reported during the summer of 2010. … The Central Mediterranean was recently affected by increased detections of Somalis, and a steady trend of Tunisians and Egyptians.”
“In Q2 2012, there were no Joint Operations running in the Central Mediterranean Sea, therefore Frontex and the FRAN community are unable to utilize intelligence obtained through the direct debriefing of migrants. However, valuable information has been obtained from interviews carried out by the Maltese authorities. Such preliminary interviews revealed that some of the Somali migrants arriving in Malta had been promised that they would be brought to Italy. They departed from an unknown location in Libya and travelled for up to three days in boats before either being intercepted by Maltese authorities or reaching the shore. The average fare was said to be around USD 1 000 per person.”
“Subsequent to the reporting period, JO Hermes 2012 was launched on 2 July and is currently planned to run until 31 October 2012 as a continuation of the deployment of JO Hermes Extension 2011, which ended just before the reporting period, on 31 March 2012. JO Hermes 2012 has been established to support the Italian authorities in tackling maritime irregular migration along the coasts of Sicily, Pantelleria and the Pelagic islands (Lampedusa, Linosa, Lampione).”
Western Mediterranean – “Detections in the Western Mediterranean were almost equally comparable to Q2 2011…”
“JO EPN Indalo 2012 started on 16 May and is currently scheduled to run until 31 October 2012. So far the number of irregular migrants apprehended in the operational areas is almost double that of the same period in 2011. Analysis of the information provided by the Spanish authorities also indicates a new increasing trend in the number of Algerian and Moroccan migrants per boat since the beginning of 2012.”
Western Africa – “[D]etections increased to a large degree, yet from lower bases, on the … Western African route (+29%).” “In the second quarter of 2012, there were just 31 detections of illegal border-crossing in this region, almost exclusively of Moroccan nationals.”
“As reported in previous FRAN Quarterlies, the Western African route from the north of Mauritania to the Western Sahara territory is being reopened by illegal migration facilitation networks. It has been inactive for years but recently an estimated 2 000 sub-Saharans (particularly from Senegal) settled in the Western Saharan coastal cities of El Aaioún and Dakhla and in the last few months ~20 000 Senegalese nationals have entered Mauritania along these routes to the north.”
“During the reporting period there was no Frontex operation relevant for the Western African Route.”
Eastern Mediterranean- “Subsequent to the reporting period (July 2012), JO EPN Aeneas 2012 was launched and is currently scheduled to run until the end of October 2012. There are two operational areas, Apulia and Calabria, covering the seashore along the Ionian Sea and part of the Adriatic Sea.”
Here are extensive excerpts from the Report with a focus on the sea borders:
“Executive summary
Taken as a whole, in Q2 2012, detections of illegal border-crossing were reduced by nearly half compared to the same quarter in 2011 due to the simultaneous effects of the winding down of the Arab Spring and fewer Albanian circular migrants entering Greece. However, detections at the undisputed long-term hotspot for irregular migration – the Greek land border with Turkey – were some 25% higher than during the same period in 2011 due to increased detections of migrants from Bangladesh and particularly Syria. [***]
In the Central Mediterranean, where detections peaked in 2011 during the Arab Spring, migrants from Somalia were increasingly detected in Malta. Specifically, in May 2012 the arrival of Somali migrants in Malta increased significantly while Italy registered a decrease in the number of Somali migrants apprehended in Sicily and the Pelagic Islands. The detected Somalis were mainly young males many of whom had been imprisoned by police or military forces during their travels through Libya. Taking into account the professional planning of the trips, it is assumed that the modus operandi has changed and that Malta is now targeted on purpose, thereby replacing Italy as the preferred destination country for this nationality. The reason for this change has not yet been confirmed; however, in the past Malta resettled some Somali migrants in the United States and in some EU Member States, which might be acting as a pull factor. Also, there is some evidence that facilitation networks located in Malta have tried to forward migrants to Sicily. [***]
The Western Mediterranean route was apparently dominated by local migrants from Morocco and Algeria but with large numbers of unknown nationalities it is assumed that local migrants were also accompanied by long-distance migrants probably from sub-Saharan Africa. In this region there was a new modus operandi involving facilitators dropping off migrants in the Chafarinas Islands, a Spanish archipelago 2 nautical miles away from the Moroccan coastline. [***]
4.1 Detections of illegal border-crossing
Overall, in Q2 2012 there were 23 092 detections of illegal border-crossing at the EU level, which is a considerable if somewhat expected seasonal increase compared to the previous quarter, and a 44% decrease compared to the same period in 2011 amidst the influx of migrants during the Arab Spring. Taken as a whole, detections of illegal border-crossing in Q2 2012 were lower than in any other second quarter since FRAN reporting began. Most probably, the low number of detections was due to the overlapping effects of the end of the Arab Spring in its initial countries (Egypt, Libya, Tunisia) and far fewer detections of circular Albanian migrants in Greece. The vast majority of detections were at the EU external land border (77%). [***]
[***] Ranked third among border sections [after the Greece-Turkey land border and the Greece-Albania border section] in Q2 2012 was the blue border of Sicily, where Tunisians, Egyptians and Somalis were increasingly detected. [***]
Figure 2 shows the evolution of the FRAN Indicator 1A – detections of illegal border-crossing, and the proportion of detections between the land and sea borders of the EU per quarter since the beginning of 2008. The second quarter of each year is usually associated with improving weather conditions more favourable for approaching and illegally crossing the external border of the EU. Moreover, conditions that are more favourable for illegal border-crossing are also more favourable for detection. The combination of these two effects tends to produce the highest number of detections during the second quarter of each year. [***]

Without question, during the second quarter of 2012 the migrants that were detected with the most increasing frequency were those from Bangladesh (+35%), Somalia (+62%), Algeria (+88%) and Syria (+639%) (Fig. 5). In fact, more migrants from Syria were detected than ever before (2 024). Detections of most of these nationalities were concentrated at the Greek land border with Turkey, with the exception of Somalis, who were mostly detected in Malta. Indeed, Somalis were particularly notable in that their detections were distributed across a very wide range of locations; as well as Malta and the Greek land border with Turkey, they were also detected in Sicily, Lampedusa and the Slovakian land border with the Ukraine. [***]
[M]igrants from Algeria were not only increasingly detected at the Greek land bor[d]er with Turkey, but also in the Spanish maritime region of Almeria and at the Romanian land border with Serbia.The latter case is assumed to represent secondary movements through the Western Balkans region.
4.2 Routes
In 2011, detections of illegal border-crossing on the Central Mediterranean route peaked briefly during the period of turbulent sociopolitical developments in North Africa, known as the Arab Spring. In contrast, on the Eastern Mediterranean route, detections have followed a remarkably seasonal pattern over the last two years. Throughout 2011 detections in the Western Mediterranean (land and sea borders with Spain) steadily increased.
As illustrated in Figure 6, the Eastern and Central Mediterranean routes reported the most detections of illegal border-crossing in the second quarter of 2012, and were characterized with seasonal increases consistent with previous years, aside the Central Mediterranean region during the Arab Spring.

In Q2 2012, there were 14 125 detections of illegal border-crossing on the Eastern Mediterranean route, an increase of 27% compared to the same period in 2011 (Fig. 6) rendering this region the undisputed hotspot for illegal entries to the EU during the current reporting period. Elsewhere, detections in the Central Mediterranean showed a seasonal increase but were much reduced (-86%) compared with the dramatic peak during the same period in 2011. Indeed, in the second quarter of 2012 detections in this region resembled the pre-Arab Spring levels reported during the summer of 2010. Detections in the
Western Mediterranean were almost equally comparable to Q2 2011, whereas detections increased to a large degree, yet from lower bases, on the Eastern Borders route (+103%), Western Balkans route (+50%) and Western African route (+29%).
These routes not only differed in their magnitudes over time but also in the composition of detected nationalities. Consistent with previous periods, detections on the Eastern Mediterranean route were dominated by migrants from Afghanistan, and more recently Bangladesh, Algeria and Syria. The Central Mediterranean was recently affected by increased detections of Somalis, and a steady trend of Tunisians and Egyptians. [***]
[T]he Western Mediterranean route was apparently dominated by local migrants from Morocco and Algeria but with large numbers of unknown nationalities it is assumed that local migrants are also accompanied by other long-distance migrants probably from sub-Saharan Africa. The exception was the much less used Western African route, which was exclusively affected by local migrants from Morocco.
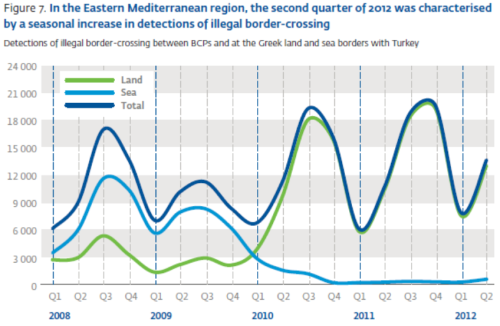
4.2.1. Eastern Mediterranean route
Since data collection began in early 2008, the Eastern Mediterranean has maintained its status as a major hotspot of irregular migration. Detections have followed a remarkably seasonal pattern invariably peaking in the third quarter of each year and concentrated at the border between Greece and Turkey, with a shift from the sea border to the land border visible in late 2009 (Fig. 7). Unusually, at the end of 2011 detections of illegal border- crossing on the Eastern Mediterranean rote remained almost constant between the third and final quarters of the year, resulting in the first recorded example of a sustained peak of detections at that time of year. This was due to an unexpected increase in detections at the Greek land border with Turkey, particularly in October. [***]
Italian Ionian Coast: For some time there has been a steady flow of Afghans and, to a lesser extent, Pakistanis arriving in the Southern Italian blue borders of Calabria and Apulia with some increases during Q2 2012.
Subsequent to the reporting period (July 2012), JO EPN Aeneas 2012 was launched and is currently scheduled to run until the end of October 2012. There are two operational areas, Apulia and Calabria, covering the seashore along the Ionian Sea and part of the Adriatic Sea.
According to Croatian open sources* in July, some 65 Asian and African migrants presumed to be heading to Italy were found drifting some 47 nautical miles south of Dubrovnik due to a broken engine (Fig. 12). They had been drifting for two days. The migrants, who had departed from Greece, did not want to be rescued by the Croatian authorities as they wanted to go to Italy. After several hours of negotiations, the authority for search and rescue towed the sailing boat to the nearest Croatian port.
There was also a recent increase in the numbers of Bangladeshis, Iraqis, Moroccans and Syrians arriving in Apulia from Greece but these detections were in much lower numbers than other nationalities. [***]
4.2.2. Central Mediterranean route
Irregular migration in the Central Mediterranean massively fluctuated in size and composition during 2011, largely due to the political and civil unrest across North Africa, particularly in Tunisia and Libya. Since Q4 2011, the situation has significantly improved following better cooperation between Italian and Tunisian authorities concerning the return of Tunisian nationals.
According to FRAN data, in Q2 2012 there were just 3 685 reported detections of illegal border-crossing on the Central Mediterranean route, a massive decrease compared to the peak in last year in Q2 2011 but an increase compared to late 2011 and early 2012. The increase was almost entirely due to more detections of migrants from Somalia (1 094) combined with a steady stream of migrants still arriving from Tunisia. Several nationalities previously detected in high numbers particularly in 2011 were not detected in significant numbers, including Bangladeshis (72) and Nigerians (19).
Migrants from Somalia – During May 2012, the arrival of Somali migrants in Malta increased significantly while
Italy registered a decrease in the number of Somali migrants apprehended in Sicily and the Pelagic Islands. In most cases, groups of males, females and minors (or families) were found on board rubber dinghies with outboard motors. A few of the boats were detected in Italian territorial waters in some distress after the migrants had called the Italian authorities for help using satellite telephones. The boats that recently headed for Malta were either intercepted by Maltese patrol boats or made it to the island without being intercepted.
Detected Somalis were mainly young males (aged 18–24) with secondary education and low or no income. The main reason for the migration was socio-economic, but in some cases it was military conflict. In Q2 2012, there were no Joint Operations running in the Central Mediterranean Sea, therefore Frontex and the FRAN community are unable to utilize intelligence obtained through the direct debriefing of migrants. However, valuable information has been obtained from interviews carried out by the Maltese authorities. Such preliminary interviews revealed that some of the Somali migrants arriving in Malta had been promised that they would be brought to Italy. They departed from an unknown location in Libya and travelled for up to three days in boats before either being intercepted by Maltese authorities or reaching the shore. The average fare was said to be around USD 1 000 per person.
Migrants from Tunisia – Most Tunisian migrants detected arriving in the Central Mediterranean Region were young (18–35 years) unmarried males with a primary level of education and low previous incomes (EUR 80–180 per month). All interviewed migrants declared to have relatives or friends already in the EU, especially in Italy, and they arrived on boats containing on average 20 migrants (Fig. 13).
Throughout the quarter, Italy and Tunisia cooperated efficiently to repatriate Tunisian nationals and so most migrants typically arrived undocumented to delay readmission. Subsequent to the reporting period, JO Hermes 2012 was launched on 2 July and is currently planned to run until 31 October 2012 as a continuation of the deployment of JO Hermes Extension 2011, which ended just before the reporting period, on 31 March 2012. JO Hermes 2012 has been established to support the Italian authorities in tackling maritime irregular migration along the coasts of Sicily, Pantelleria and the Pelagic islands (Lampedusa, Linosa, Lampione).
4.2.3. Western Mediterranean route
Irregular migration in the Western Mediterranean region increased throughout 2011 from just 890 detections in Q1 2011 to 3 568 detections in Q3. In Q2 2012, there were 1 549 detections which almost exactly corresponds to the number of detections the year before in Q2 2011 (1 569). As was the case a year ago, most detections were of Algerians followed by migrants of unknown nationalities (presumed to be sub-Saharan Africans) and Moroccans.
Recently, the size of the sub-Saharan population coming from Algeria has increased in different settlements adjacent to the Melilla border fence. Criminal networks operate more easily in this north eastern region of Morocco and the Spanish authorities treat a large-scale illegal crossing of the fence to the Spanish side as a real possibility. Attempts to cross have been made in the past involving groups of dozens or even hundreds.
JO EPN Indalo 2012 started on 16 May and is currently scheduled to run until 31 October 2012. So far the number of irregular migrants apprehended in the operational areas is almost double that of the same period in 2011. Analysis of the information provided by the Spanish authorities also indicates a new increasing trend in the number of Algerian and Moroccan migrants per boat since the beginning of 2012. The improvement of the weather and sea conditions during the reporting period impacted on the number of boats detected, with a gradual increase of the number of arrivals during the peak period, which according to data from the last two years is from May to October.
Migrants from Algeria – According to information gathered during interviews, most Algerians were single male adults aged 19–36 on average, but there were also a few females and minors in good health. Most migrants belonged to the lower middle class and, despite having a high level of education compared to sub-Saharan nationals, they suffered from a generalised lack of opportunities, welfare and access to public health services. Nearly all the Algerian migrants spoke Arabic with a few French and English speakers, but all were undocumented to avoid repatriation after arriving in Spain. The majority had relatives or friends in EU Member States, mainly in France and Spain, who could help them to find a job and settle within the ethnic communities already established in these countries.
4.2.4. Western African route
In the second quarter of 2012, there were just 31 detections of illegal border-crossing in this region, almost exclusively of Moroccan nationals.
As reported in the previous FRAN Quarterly*, in February 2012 Moroccan and Spanish Ministers of Interior signed a police agreement to create two joint police stations in the Spanish (Algeciras) and Moroccan (Tangiers) territories to cooperate by exchanging operational information and best practices between different police services. The goal of this cooperation is to strengthen the efforts and improve the results against organized crime operating on both sides of the Strait of Gibraltar involved in the smuggling of drugs, international terrorism, irregular migration and trafficking in human beings.
Following these developments, both International Police Cooperation Centres became operational during May 2012 (Fig. 14). The International Joint Police Stations are going to be integrated with National Police / Guardia Civil (Spain) and General Direction for National Security (Police) / Royal Gendarmerie (Morocco) staff for a rapid and effective exchange of information.
As reported in previous FRAN Quarterlies, the Western African route from the north of Mauritania to the Western Sahara territory is being reopened by illegal migration facilitation networks. It has been inactive for years but recently an estimated 2 000 sub-Saharans (particularly from Senegal) settled in the Western Saharan coastal cities of El Aaioún and Dakhla and in the last few months ~20 000 Senegalese nationals have entered Mauritania along these routes to the north.
During the reporting period there was no Frontex operation relevant for the Western African Route. [***]”

Click here or here for Report.
















