 The Frontex Risk Analysis Unit (RAU) released its 3rd Quarter Report (July-September) for 2011 on 18 January. (See also 2nd Quarter Report (April-June 2011) and 1st Quarter Report (Jan-March 2011).) The reports contain a significant amount of information, graphs, and statistical tables regarding detections of illegal border crossings, irregular migration routes, detections of facilitators, detections of illegal stays, refusals of entry, asylum claims, and more.
The Frontex Risk Analysis Unit (RAU) released its 3rd Quarter Report (July-September) for 2011 on 18 January. (See also 2nd Quarter Report (April-June 2011) and 1st Quarter Report (Jan-March 2011).) The reports contain a significant amount of information, graphs, and statistical tables regarding detections of illegal border crossings, irregular migration routes, detections of facilitators, detections of illegal stays, refusals of entry, asylum claims, and more.
The Report is based on data provided by Member States. The Report states that “Frontex and the Member States are currently harmonising their illegal-migration data, a process that is not yet finalised. Therefore more detailed data and trends in this report should be interpreted with caution and, where possible, cross-referenced with information from other sources.”
Here are extensive excerpts from the Q3 Report:
“Executive summary – In Q3 2011 most indicators monitored within FRAN community increased compared to a year ago. For example, detections of illegal border-crossing and refusals of entry both reached much higher levels than in Q3 2010. Moreover, more applications for international protection were submitted than in any other quarter since data collection began in 2008. Consistent with recent years, the majority of illegal border-crossings were limited to a small number of hotspots of irregular migration such as the Eastern and Central Mediterranean routes, accounting for 50% and 33% of the EU total, respectively. However, in Q3 2011 there was also a rise in the importance of the Western Mediterranean route, now representing nearly 10% of the EU total. At the EU level, the most commonly detected migrants were from Afghanistan, yet due to the recent increases in the number of migrants from Pakistan and Nigeria (by seven and ten times compared to Q3 2010, respectively) these nationalities have moved to the second and third position.
In Q3 2011 there were 19 266 detections of illegal border-crossing in the Eastern Mediterranean, a seasonal increase to a level almost exactly comparable with the same period in 2010. As was the case throughout 2010, detections were concentrated at the Greek land border with Turkey, where Afghans accounted for nearly half of all detected migrants. However, at this border section detections of migrants from Pakistan increased massively compared to last year and now rank second….
In contrast to the consistent wave of irregular migration in the Eastern Mediterranean, the situation in the Central Mediterranean has been volatile in 2011, dependent on the political developments and civil unrest across North Africa. For example, civil unrest in this region, particularly in Tunisia, led to a dramatic increase in detections in the Central Mediterranean early in 2011. Consequently, in March 2011 some 14 400 Tunisian migrants arrived in the Italian island of Lampedusa. In April an accelerated repatriation agreement was signed between Italy and Tunisia, which resulted in a 75% reduction in the flow of Tunisians, but the region was then inundated by large numbers of sub-Saharan migrants arriving in Lampedusa, Sicily and Malta, many having been forcibly expelled from Libya by the Gaddafi regime. Since the National Transitional Council successfully gained control of Libya, this flow stopped abruptly in August. However, in Q3 2011 there were 12 673 detections of illegal border-crossing on this route, where Tunisian and sub-Saharan migrants, particularly Nigerians, are still arriving in significant numbers.
In Q3 2011 there were more detections in the Western Mediterranean (3 568) since mid 2008. A wide range of migrants from North African and sub-Saharan countries were increasingly detected in this region. However, it is difficult to analyse the exact composition of the flow as the number of migrants of unknown nationality on this route doubled compared to the previous quarter. This may indicate an increasing proportion of nationalities that are of very similar ethnicity and/or geographic origin.
The flows of migrants arriving in the EU had a significant effect on the number of applications for international protection submitted: in Q3 2011 there were a massive 64 801 applications submitted across Member States. The largest increases in submitted applications were reported by Italy and involved nationals of Nigeria, Ghana, Mali and Pakistan. However, the applications submitted by nationals of Pakistan and Afghanistan also increased across a wide range of other Member States, such as Germany and Austria. In contrast to increasing applications for international protection were fewer detections of facilitators of irregular migration than ever before. This widespread and long decline may be because organized crime groups are increasingly recruiting would-be migrants by offering them legitimate entry to the EU with false or fraudulently obtained documentation. This is less risky and carries lower detection probability for facilitators than, for example, accompanying migrants across the border….
[***]
4.1 Detections of illegal border-crossing – [ … ] The third quarter of each year is usually associated with weather conditions favourable for approaching and illegally crossing the external border of the EU. Correspondingly, conditions that are favourable for illegal border-crossings are also more conducive to detecting them. The combination of these two effects resulted in the highest number of detections in each of the last few years being reported in Q3 2011. In contrast, in 2011 detections were higher in the second than in the third quarter, because of exceptionally high detections in the first half of 2011, rather than particularly low detections in Q3 2011. At the sea border, there were 15 418 detections which is a 44% reduction compared to Q2 2011, but a fivefold increase compared to Q3 2010. In contrast, there were 23 079 detections at the land border which was a 68% increase compared to the preceding quarter, but a 22% reduction compared to Q3 2010. Hence, detections decreased at the sea border, particularly in Italy, and increased at the land border to a level comparable to 2010….
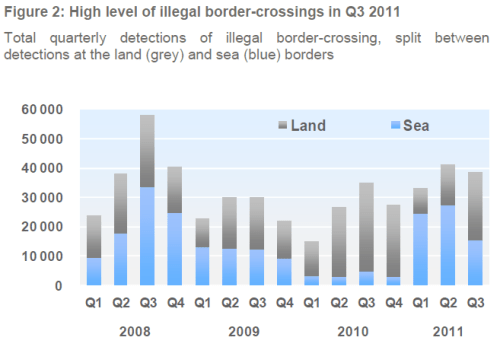 [… ] In the first half of 2011 the situational picture of irregular migration to the EU was dominated by illegal border-crossings reported by Italy. This influx was due to a surge of Tunisians in Q1 and sub-Saharan African migrants in Q2 arriving in the Italian island of Lampedusa in the wake of major civil unrest in North Africa (the so-called Arab Spring), which has now, to some extent, decipitated. Hence, in Q3 2011 detections in Italy halved compared to the previous two quarters yet remained some six times higher than during the same period last year.
[… ] In the first half of 2011 the situational picture of irregular migration to the EU was dominated by illegal border-crossings reported by Italy. This influx was due to a surge of Tunisians in Q1 and sub-Saharan African migrants in Q2 arriving in the Italian island of Lampedusa in the wake of major civil unrest in North Africa (the so-called Arab Spring), which has now, to some extent, decipitated. Hence, in Q3 2011 detections in Italy halved compared to the previous two quarters yet remained some six times higher than during the same period last year.
At the EU level the most commonly detected migrants came from Afghanistan, constituting a quarter of all detections despite a 15% decrease compared to the previous year (Fig. 3). The majority of Afghan migrants were detected at the border between Greece and Turkey, with the remaining mostly detected at the southern Italian blue border. Throughout 2010 the most commonly detected migrants were from Albania (mostly circular migrants to Greece), representing 25–45% of the EU total, although in many cases individuals may have been detected several times within a given period. However, in Q3 2011 detections of Albanians fell to negligible levels following their visa-free status for travel to the EU granted in December 2010 (Fig. 3).
Without question, detections of migrants from Pakistan and Tunisia have increased more than any other nationality over the last year (Fig. 3). In the case of migrants from Pakistan, in Q3 2011 most were detected at the border between Greece and Turkey, followed by the southern Italian blue border. This detection profile almost exactly mirrors that of migrants from Afghanistan. In contrast, migrants from Tunisia are almost exclusively detected in Italy, followed by Greece. Although detections of migrants from Tunisia increased dramatically compared with a year ago, they fell massively compared to the peak in Q1 2011.
Another notable phenomenon is the increased rate of migrants from Nigeria detected at the blue border (Fig. 3) mostly in Italy, with some evidence for increasing numbers in southern Spain. In the former case most departed from Tunisia, while in Spain most departed from Morocco. This trend is related to the threefold increase in the number of asylum applications submitted by Nigerian migrants almost exclusively in Italy.
Routes – As illustrated in Figure 4, during the first half of 2011 detections of illegal bordercrossing on the Central Mediterranean route, which comprises the blue borders of Italy and Malta, dramatically increased and exceeded those reported from the Eastern Mediterranean route, which is made up of the land and sea borders of Greece, Bulgaria and Cyprus. However, in Q3 2011 detections on the Eastern Mediterranean route, by following a remarkably seasonal pattern, similar to that of 2010, once more exceeded detections on the Central Mediterranean route, where detections fell dramatically compared with the peak in the first six months of 2011.
These routes not only differed in their trends over time but also in the composition of detected nationalities. For example, detections on the Eastern Mediterranean route have, for the last year at least, comprised of large numbers of Asian, North African and sub-Saharan nationalities including increased detections of migrants from Pakistan. In contrast, nationalities detected in the Central Mediterranean have evolved throughout 2011. In Q1 2011 mostly Tunisians were detected after they had departed from their own country; in Q2 2011 reduced but still significant numbers of Tunisians were joined by mix of sub-Saharan Africans, many of whom were forcibly expelled from Libya. In the current reporting period detections of Tunisians remained stable, yet the number of sub-Saharan Africans decreased. Figure 4 also shows that in Q3 2011 detections on the Western Mediterranean route increased, mostly of migrants of unknown nationalities but also of Algerians and Nigerians.
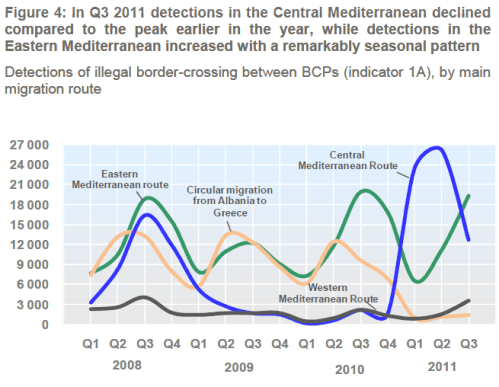 4.1.1 Eastern Mediterranean route – Since data collection began in early 2008, the Eastern Mediterranean has maintained its status as a hotspot of irregular migration. Detections have followed a remarkably seasonal pattern invariably peaking in the third quarter of each year, being concentrated at the border between Greece and Turkey with a shift from the sea border to the land border in early 2010. Afghan migrants have consistently featured highly on the list of most detected nationalities. In 2010 there was an increase in Algerian migrants that has since subsided, but more recently there has been a massive increase in the number of migrants from Pakistan detected on this route.
4.1.1 Eastern Mediterranean route – Since data collection began in early 2008, the Eastern Mediterranean has maintained its status as a hotspot of irregular migration. Detections have followed a remarkably seasonal pattern invariably peaking in the third quarter of each year, being concentrated at the border between Greece and Turkey with a shift from the sea border to the land border in early 2010. Afghan migrants have consistently featured highly on the list of most detected nationalities. In 2010 there was an increase in Algerian migrants that has since subsided, but more recently there has been a massive increase in the number of migrants from Pakistan detected on this route.
In the current reporting period, detections of illegal border-crossing on this route increased seasonally and in line with previous years, almost exclusively due to a massive increase in detections at the Greek land border with Turkey, where detections increased from 10 464 to 18 509 over the same period. Based on seasonal pattern of detections in previous years, the increase in pressure on this route during Q3 2011 was not entirely unexpected and reached a level almost exactly comparable to that of a year ago. Indeed, according to data collected during JO Poseidon the average number of detections per day immediately subsequent to the current reporting period exceed that during the same period in 2010, immediately prior to the deployment of the first JO RABIT 2010….
[***]
4.1.2 Central Mediterranean route – Irregular migration in the Central Mediterranean has fluctuated in size and composition during 2011, depending on the political and civil unrest across North Africa. Initially detections in the Central Mediterranean massively increased in early 2011 due to civil unrest in the region, particularly in Tunisia, Libya and, to a lesser extent, Egypt. As a result, in Q1 some 20 000 Tunisian migrants arrived on the Italian island of Lampedusa. In Q2 2011 the flow of Tunisian migrants was reduced by 75% following an accelerated repatriation agreement that was signed between Italy and Tunisia. However, the region was then inundated by large numbers of sub-Saharan migrants detected across the region, many claiming to have been forcibly expelled from Libya by the Gaddafi regime. In the current reporting period irregular migration in the region has eased somewhat due to democratic elections* in Tunisia and the National Transitional Council successfully gaining control of Libya. However in Q3 2011 arrivals increased from Egypt and subsequent to the reporting period there was some indication that the flow from Libya has been reinstated.
According to the FRAN data, in Q3 2011 there were more than 12 500 reported detections of illegal border-crossing on the Central Mediterranean route, a 50% decrease compared to the ‘peak’ reported during the first and second quarter of 2011, but still massively increased compared to the background detections throughout all of 2010. Most detections in the Central Mediterranean region were reported from the Italian Pelagic Islands, where detections also fell by a half compared to the previous quarter. In some areas the decrease was even more marked. For example, in Sicily detections fell by 75% such that in Q3 2011 a stable trend of Egyptians and Tunisians constituted nearly all detections. Detections ell to an even greater extent in Malta.
4.1.3 Western Mediterranean route – Irregular migration across the Western Mediterranean towards southern Spain was at a low level through most of 2010 averaging just over a thousand detections per quarter. However, pressure has been steadily increasing throughout 2011 until the current reporting period when there were more than 3 500 detections of illegal border-crossing – an increase of two thirds compared to Q3 2010. As a result, the Western Mediterranean is now the third largest point of entry for illegal bordercrossing into the EU. The most common and the most increasingly detected migrants were of unknown nationalities, followed by migrants local to the region from Algeria and Morocco. There were also significant increases in migrants from further afield such as Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Nigeria and Congo.
4.1.4 Western African route – The cooperation and bilateral agreements between Spain and the rest of the Western African countries (Mauritania, Senegal and Mali) are developing steadily. They are one of the main reasons for the decrease in arrivals on this route over the last year, as is the presence of patrolling assets near the African coast. Despite a slight increase in Q4 2010, detections on this route remained low and totalled at just 50 detections of exclusively Moroccan migrants in Q3 2011.
[***]”
Click here for Frontex Press Statement.
Click here for Q3 Report.
Click here for previous post on Q1 and Q2 Reports.









