Frontex’s Annual Risk Analysis (ARA) for 2010 was prepared in March 2010 and was posted to the Frontex web site on 7 July. The public document only contains certain portions of the full ARA as recommendations and other “operationally sensitive details” have been redacted. While some of the ARA’s contents have previously been released by Frontex, this 35 page document contains a lot of data regarding irregular migration by land, sea, and air, and is worth a read.
Frontex’s Annual Risk Analysis (ARA) for 2010 was prepared in March 2010 and was posted to the Frontex web site on 7 July. The public document only contains certain portions of the full ARA as recommendations and other “operationally sensitive details” have been redacted. While some of the ARA’s contents have previously been released by Frontex, this 35 page document contains a lot of data regarding irregular migration by land, sea, and air, and is worth a read.
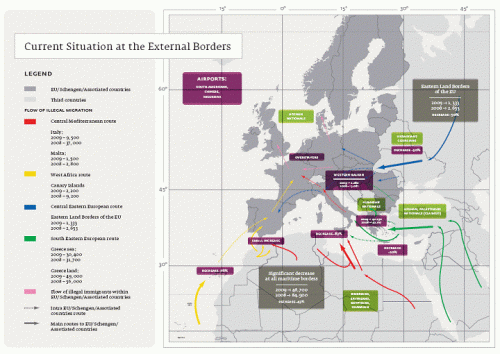
Excerpts from the ARA relating to maritime migration include:
“Detections of illegal border crossing – In 2009, the [EU] Member States and Schengen Associated Countries reported a total of 106,200 detections of illegal border crossings at the sea and land borders of the EU. This represented a 33% decrease compared to 2008. The decrease is comprised of both a strong decrease reported from the sea borders (-23%), and land borders (-43%).”
“The bilateral collaboration agreements with third countries of departure on the Central Mediterranean route (Italy with Libya) and the Western African route (which Spain signed with Senegal and Mauritania) had an impact on reducing departures of illegal migrants from Africa.”
“The agreements were made at a time when the economic crisis decreased the labour demand in the EU, thus simultaneously reducing the pull factor. The synchronisation of these events probably explains why no displacement has so far been noticed from the Central Mediterranean and Western African routes to other illegal migration routes in the statistics for detections.”
“However, intelligence suggests that the risk of displacement remains high, either with the emergence of new routes or the exploitation of existing ones by nationalities which used to be detected along the Central Mediterranean or the Western African routes.”
“As a corollary to the sharp decreases registered in Italy and Spain, the number of detections of illegal border crossing in Greece rose from 50% of the total EU detections to 75% of the total. In 2009, the Greek land border sections with Albania and FYROM represented the largest share of the EU total, with 36,600 detections (34% of the EU total), followed by 22,000 detections in the Aegean Sea with (21% of the EU total).”
“Eastern Mediterranean route – The Eastern Mediterranean route is the route taken by illegal migrants transiting through Turkey and entering the EU through eastern Greece, southern Bulgaria or Cyprus. Turkey, due to its geographical position near the EU, is the main nexus point on this route. From Istanbul, illegal migrants may reach the Greek islands in the Aegean Sea, or cross the land borders to Greece or to Bulgaria.”
“In 2009, illegal border crossing on the Eastern Mediterranean route totalled 41,500, or 39% of all EU detections. Most of the detections were reported from the Aegean Sea, followed by detections along the land border between Turkey and Greece. The number of detections reported by Bulgaria and Cyprus were considerably lower.”
“Central Mediterranean route – The Central Mediterranean route refers to illegal migration from northern Africa to Italy and to Malta. For the past two years, Libya has been a nexus point where migrants from the Horn of Africa and Western African routes and a small proportion of Asian nationals met before embarking.”
“Since the signing of a bilateral agreement with Libya, joint patrols by Libya and Italy have had a clear and measurable deterrent effect, with 3,200 detections in the seven months after the joint patrols (June to December), compared to 7,200 detections in the five months before the joint patrols (January to May), and almost 40,000 detections in the whole of 2008.”
“Western African route – The Western African route is primarily through Western African countries to Spain via the Canary Islands. The main embarkation points are in Senegal and Mauritania and the main countries of origin are Mali, Mauritania, Guinea Conakry and Senegal. Other African nationals have also been reported, and occasionally migrants from Asia. This route is now less favoured since the Spanish collaboration agreements with Senegal and Mauritania. The Frontex coordinated Joint Operation Hera plays a major role in maintaining effective surveillance in the area.”
“The Western Mediterranean route includes the sea route from Northern Africa to the Iberian Peninsula, and the land route through Ceuta and Melilla. It is mostly used by Northern African nationals (Algerian and Moroccan) travelling to Spain, France and Italy.”
“Maritime detections between Northern Africa and Spain are rising, with increasing detections of Algerian and to a lesser extent Sub Saharan nationals. Moroccan nationals are also regularly detected on this route. The lack of employment opportunities for the growing population of young people in Morocco continues to increase the incentives of migrating to the EU. The Spanish authorities recently reported an increasing number of attempts by Moroccan minors to get on the ferry link between Tanger and Spain. These cases do not seem connected with criminal networks; rather individual attempts are driven by poor employment prospects in Morocco.”
Click here for the ARA.
Click here for link to Frontex Map showing situation at External Borders.
 [ARA page 18]
[ARA page 18]
 [ARA page 13]
[ARA page 13]